Brazier
(khet)
Appearance: A brazier was a four-lobed portable ritual grill used in funerary offerings. The grill was lifted by the lobes and thus the user was able to move it without being burned. The hieroglyph depicts the brazier with its lobes and a stylized flame. The lobe in the rear is hidden by the flame.
Meaning: The brazier was the determinative in the Egyptian language for many words related to fire and heat, for example: "fire", "flame", "hot" and "candle". It was a symbol of fire in Egyptian art and of fire's connotations. Fire was a mysterious and potent entity in many ancient cultures. It is found depicted frequently in Egyptian art.
Fire seems to have a life force of its own and thus was a symbol itself for life. At the sed festival, which renewed and gave new life to his reign in Egypt, the pharoah would light a symbolic fire. The sun was seen as the "fire of life". The uraeus, a symbol of the sun, was often portrayed spitting fire at the sun's enemies. Heliopolis, whose name literally means "city of the sun" was sometimes represented by a brazier. A pair of braziers represented the "Island of Fire" where the sun was born. This island was also a metaphor for the dawn.
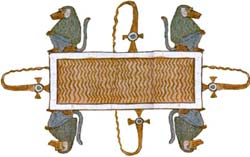
Fire was also closely related to the Underworld. Much like the medieval Christian concept of Hell, the Egyptian Underworld was filled with fiery rivers and lakes. The Underworld was also inhabited by many fire demons who threatened the wicked dead. These demons wear depicted with the hieroglyph of the brazier on their heads. The Lakes of Fire in the Underworld were drawn like normal pools of water, but with braziers on each side and fiery red (instead of blue) wavy lines transversing them. The Lakes of Fire were also shown with baboons seated at each corner. These lakes were only troublesome for the wicked, the righteous could drink of them and be refreshed. The righteous could also transform into shooting flames and destroy their enemies.
Fire was also a protective element to the Egyptians. Protective deities such as Tauret would sometimes wield torches and braziers to ward off evil.
A similar hieroglyph shows an incense bowl or lamp with a flame (![]() ).
This glyph was used as a substitute for the brazier. It was also used
as an amulet to protect the deceased.
).
This glyph was used as a substitute for the brazier. It was also used
as an amulet to protect the deceased.
Digg This!
![]() Del.icio.us
Del.icio.us
![]() Stumble Upon
Stumble Upon
